| Original TOGAF 9 Text for Phase D: Technology Architecture |
|
|
| Related Elements |
|---|
This chapter describes the development of a Technology Architecture for an architecture project. 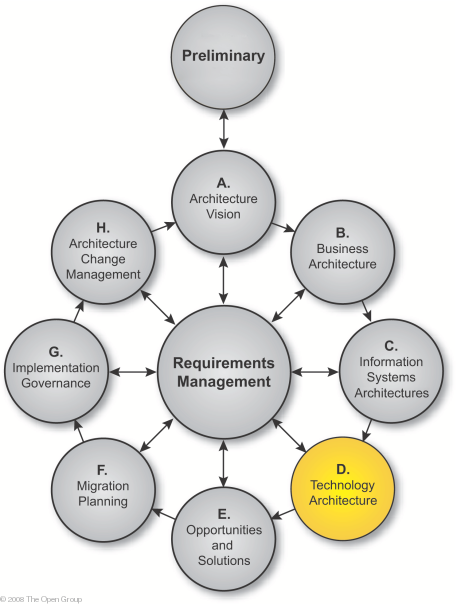
ObjectivesThe Technology Architecture phase seeks to map application components defined in the Application Architecture phase into a set of technology components, which represent software and hardware components, available from the market or configured within the organization into technology platforms. As Technology Architecture defines the physical realization of an architectural solution, it has strong links to implementation and migration planning. Technology Architecture will define baseline (i.e., current) and target views of the technology portfolio, detailing the roadmap towards the Target Architecture, and to identify key work packages in the roadmap. Technology Architecture completes the set of architectural information and therefore supports cost assessment for particular migration scenarios. ApproachArchitecture RepositoryAs part of Phase D, the architecture team will need to consider what relevant Technology Architecture resources are available in the Architecture Repository (see Part V, Architecture Repository ). In particular:
InputsThis section defines the inputs to Phase D. Reference Materials External to the Enterprise
Non-Architectural InputsArchitectural Inputs
StepsThe level of detail addressed in Phase D will depend on the scope and goals of the overall architecture effort. New technology building blocks being introduced as part of this effort will need to be defined in detail during Phase D. Existing technology building blocks to be supported in the target environment may need to be redefined in Phase D to ensure interoperability and fit-for-purpose within this specific Technology Architecture. The order of the steps in Phase D (see below) as well as the time at which they are formally started and completed should be adapted to the situation at hand in accordance with the established architecture governance. In particular, determine whether in this situation it is appropriate to conduct Baseline Description or Target Architecture development first, as described in Part III, Applying Iteration to the ADM . All activities that have been initiated in these steps must be closed during the Finalize the Technology Architecture step (see Finalize the Technology Architecture). The documentation generated from these steps must be formally published in the Create Architecture Definition Document step (see Create Architecture Definition Document). The steps in Phase D are as follows:
1. Select Reference Models, Viewpoints, and ToolsReview and validate the set of technology principles. These will normally form part of an overarching set of architecture principles. Guidelines for developing and applying principles, and a sample set of application principles, are given in Part III, Architecture Principles . Select relevant Technology Architecture resources (reference models, patterns, etc.) from the Architecture Repository (see Part V, Architecture Repository), on the basis of the business drivers, stakeholders, and their concerns. Select relevant Technology Architecture viewpoints that will enable the architect to demonstrate how the stakeholder concerns are being addressed in the Technology Architecture. Identify appropriate tools and techniques to be used for capture, modeling, and analysis, in association with the selected viewpoints. Depending on the degree of sophistication required, these may comprise simple documents and spreadsheets, or more sophisticated modeling tools and techniques. Determine Overall Modeling ProcessFor each viewpoint, select the models needed to support the specific view required, using the selected tool or method. Ensure that all stakeholder concerns are covered. If they are not, create new models to address them, or augment existing models (see above). The process to develop a Technology Architecture incorporates the following steps:
In the earlier phases of the ADM, certain decisions made around service granularity and service boundaries will have implications on the technology component and the platform service. The areas where the Technology Architecture may be impacted will include the following:
Product selection processes may occur within the Technology Architecture phase where existing products are re-used, incremental capacity is being added, or product selection decisions are a constraint during project initiation. Where product selection deviates from existing standards, involves significant effort, or has wide-ranging impact, this activity should be flagged as an opportunity and addressed through the Opportunities & Solutions phase. Identify Required Catalogs of Technology Building BlocksCatalogs are inventories of the core assets of the business. Catalogs are hierarchical in nature and capture a decomposition of a metamodel entity and also decompositions across related model entities (e.g., platform service -> logical technology component -> physical technology component). Catalogs form the raw material for development of matrices and diagrams and also act as a key resource for portfolio managing business and IT capability. The Technology Architecture should create technology catalogs as follows:
The following catalogs should be considered for development within a Technology Architecture:
The structure of catalogs is based on the attributes of metamodel entities, as defined in Part IV, Content Metamodel . Identify Required MatricesMatrices show the core relationships between related model entities. Matrices form the raw material for development of diagrams and also act as a key resource for impact assessment. The following matrix should be considered for development within a Technology Architecture:
Identify Required DiagramsDiagrams present the Technology Architecture information from a set of different perspectives (viewpoints) according to the requirements of the stakeholders. This activity provides a link between platform requirements and hosting requirements, as a single application may need to be physically located in several environments to support local access, development lifecycles, and hosting requirements. For major baseline applications or application platforms (where multiple applications are hosted on the same infrastructure stack), produce a stack diagram showing how hardware, operating system, software infrastructure, and packaged applications combine. If appropriate, extend the Application Architecture diagrams of software distribution to show how applications map onto the technology platform. For each environment, produce a logical diagram of hardware and software infrastructure showing the contents of the environment and logical communications between components. Where available, collect capacity information on the deployed infrastructure. For each environment, produce a physical diagram of communications infrastructure, such as routers, switches, firewalls, and network links. Where available, collect capacity information on the communications infrastructure. The following diagrams should be considered for development within a Technology Architecture:
The structure of diagrams is based on the attributes of metamodel entities, as defined in Part IV, Content Metamodel . Identify Types of Requirement to be CollectedOnce the Technology Architecture catalogs, matrices, and diagrams have been developed, architecture modeling is completed by formalizing the data-focused requirements for implementing the Target Architecture. Within this step, the architecture engagement should identify types of requirement that must be met by the architecture implementation, including:
Select ServicesThe services portfolios are combinations of basic services from the service categories in the TOGAF TRM that do not conflict. The combination of services are again tested to ensure support for the applications. This is a pre-requisite to the later step of defining the architecture fully. The previously identified requirements can provide more detailed information about:
Where requirements demand definition of specialized services that are not identified in TOGAF, consideration should be given to how these might be replaced if standardized services become available in the future. For each building block, build up a service description portfolio as a set of non-conflicting services. The set of services must be tested to ensure that the functionality provided meets application requirements. 2. Develop Baseline Technology Architecture DescriptionDevelop a Baseline Description of the existing Technology Architecture, to support the Target Technology Architecture. The scope and level of detail to be defined will depend on the extent to which existing technology components are likely to be carried over into the Target Technology Architecture, and on whether architectural descriptions exist, as described in Approach. Identify the relevant Technology Architecture building blocks, drawing on any artifacts held in the Architecture Repository. If nothing exists within the Architecture Repository, define each application in line with the Technology Portfolio catalog (see Part IV, Content Metamodel). Begin by converting the description of the existing environment into the terms of the organization's Foundation Architecture (e.g., the TOGAF Foundation Architecture's TRM). This will allow the team developing the architecture to gain experience with the model and to understand its component parts. The team may be able to take advantage of a previous architectural definition, but it is assumed that some adaptation may be required to match the architectural definition techniques described as part of this process. Another important task is to set down a list of key questions which can be used later in the development process to measure the effectiveness of the new architecture. Where new architecture models need to be developed to satisfy stakeholder concerns, use the models identified within Step 1 as a guideline for creating new architecture content to describe the Baseline Architecture. 3. Develop Target Technology Architecture DescriptionDevelop a Target Description for the Technology Architecture, to the extent necessary to support the Architecture Vision, Target Business Architecture, and Target Information Systems Architecture. The scope and level of detail to be defined will depend on the relevance of the technology elements to attaining the Target Architecture, and on whether architectural descriptions exist. To the extent possible, identify the relevant Technology Architecture building blocks, drawing on the Architecture Repository (see Part V, Architecture Repository). A key process in the creation of a broad architectural model of the target system is the conceptualization of building blocks. Architecture Building Blocks (ABBs) describe the functionality and how they may be implemented without the detail introduced by configuration or detailed design. The method of defining building blocks, along with some general guidelines for their use in creating an architectural model, is described in Part IV, Building Blocks and the ADM , and illustrated in detail in Building Blocks Example). Where new architecture models need to be developed to satisfy stakeholder concerns, use the models identified within Step 1 as a guideline for creating new architecture content to describe the Target Architecture. 4. Perform Gap AnalysisFirst, verify the architecture models for internal consistency and accuracy. Note changes to the viewpoint represented in the selected models from the Architecture Repository, and document. Test architecture models for completeness against requirements. Identify gaps between the baseline and target:
5. Define Roadmap ComponentsFollowing creation of a Baseline Architecture, Target Architecture, and gap analysis, a Technology Roadmap is required to prioritize activities over the coming phases. This initial Technology Architecture roadmap will be used as raw material to support more detailed definition of a consolidated, cross-discipline roadmap within the Opportunities & Solutions phase. 6. Resolve Impacts Across the Architecture LandscapeOnce the Technology Architecture is finalized, it is necessary to understand any wider impacts or implications. At this stage, other architecture artifacts in the Architecture Landscape should be examined to identify:
7. Conduct Formal Stakeholder ReviewCheck the original motivation for the architecture project and the Statement of Architecture Work against the proposed Technology Architecture, asking if it is fit for the purpose of supporting subsequent work in the other architecture domains. Refine the proposed Technology Architecture only if necessary. 8. Finalize the Technology Architecture
9. Create Architecture Definition DocumentDocument the rationale for building block decisions in the Architecture Definition Document. Prepare the technology sections of the Architecture Definition Document, comprising some or all of:
If appropriate, use reports and/or graphics generated by modeling tools to demonstrate key views of the architecture. Route the document for review by relevant stakeholders, and incorporate feedback. OutputsThe outputs of Phase D are:
PostscriptChoosing the scope of an architecture development cycle carefully will accelerate the pay-back. In contrast, an excessively large scope is unlikely to lead to successful implementation. |
The Open Group gratefully acknowledge Capgemini for the creation of the Eclipse Process Framework Method Plugin for TOGAF9. Downloads of the TOGAF documentation, are available under license from the TOGAF information web site. The license is free to any organization wishing to use TOGAF entirely for internal purposes (for example, to develop an information system architecture for use within that organization). A book is also available (in hardcopy and pdf) from The Open Group Bookstore as document G091.
Copyright © 1999-2009 The Open Group, All Rights Reserved |